The Science Behind Porosity: A Comprehensive Guide for Welders and Fabricators
Recognizing the detailed mechanisms behind porosity in welding is essential for welders and producers making every effort for impressive craftsmanship. From the composition of the base products to the complexities of the welding process itself, a multitude of variables conspire to either aggravate or reduce the presence of porosity.
Understanding Porosity in Welding
FIRST SENTENCE:
Evaluation of porosity in welding reveals vital insights into the honesty and top quality of the weld joint. Porosity, identified by the presence of dental caries or spaces within the weld metal, is an usual worry in welding procedures. These voids, otherwise appropriately addressed, can compromise the structural stability and mechanical properties of the weld, causing possible failures in the completed product.

To identify and evaluate porosity, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic screening or X-ray evaluation are frequently used. These methods permit for the recognition of inner flaws without compromising the stability of the weld. By examining the dimension, shape, and circulation of porosity within a weld, welders can make enlightened choices to enhance their welding procedures and accomplish sounder weld joints.
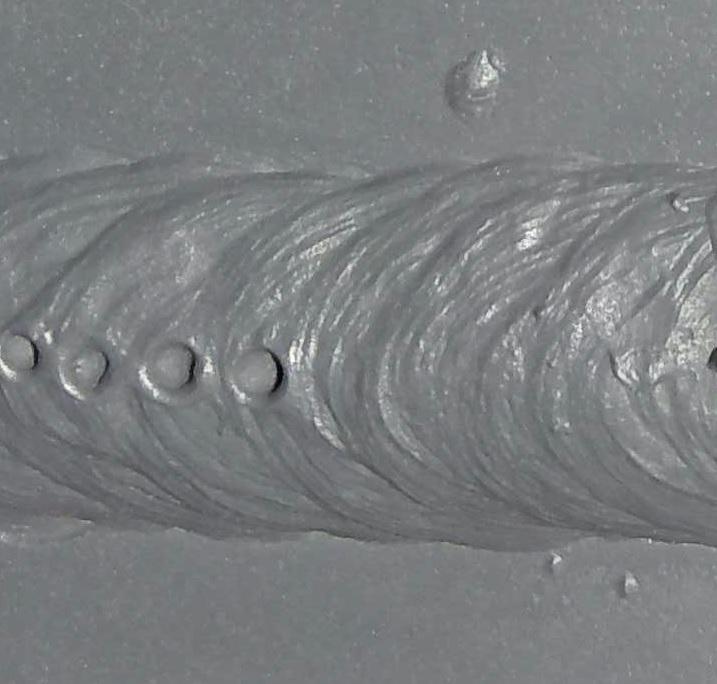
Factors Affecting Porosity Development
The incident of porosity in welding is influenced by a myriad of factors, varying from gas shielding performance to the complexities of welding criterion setups. One vital element contributing to porosity development is poor gas shielding. When the securing gas, normally argon or CO2, is not successfully covering the weld swimming pool, climatic gases like oxygen and nitrogen can contaminate the molten steel, bring about porosity. In addition, the sanitation of the base materials plays a significant role. Pollutants such as rust, oil, or moisture can evaporate during welding, producing gas pockets within the weld. Welding parameters, consisting of voltage, current, travel speed, and electrode kind, additionally influence porosity formation. Making use of improper setups can produce too much spatter or warm input, which subsequently can cause porosity. Furthermore, the Learn More welding method used, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or protected metal arc welding (SMAW), can affect porosity development due to variants in warmth circulation and gas insurance coverage. Understanding and managing these variables are crucial for reducing porosity in welding procedures.
Results of Porosity on Weld High Quality
Porosity formation dramatically compromises the structural integrity and mechanical residential or commercial properties of welded joints. When porosity exists in a weld, it creates spaces or dental caries within the product, minimizing the general toughness of the joint. These gaps serve as stress focus points, making the weld much more vulnerable to cracking and failure under tons. The existence of porosity additionally damages the weld's resistance to rust, as the entraped air or gases within deep spaces can respond with the surrounding setting, resulting in deterioration my sources over time. Furthermore, porosity can impede the weld's ability to stand up to stress or impact, additional endangering the overall high quality and dependability of the bonded structure. In important applications such as aerospace, automobile, or architectural buildings, where safety and security and sturdiness are critical, the damaging effects of porosity on weld top quality can have serious repercussions, highlighting the relevance of lessening porosity through proper welding techniques and treatments.
Methods to Reduce Porosity
Additionally, making use of the ideal welding parameters, such as the proper voltage, current, and take a trip speed, is crucial in protecting against porosity. Keeping a regular arc length and angle throughout welding additionally assists lower the probability of porosity.

Using the appropriate welding technique, such as back-stepping or employing a weaving motion, can also assist distribute warmth equally and lower the possibilities of porosity development. By executing these methods, welders can efficiently reduce porosity and create high-quality welded joints.

Advanced Solutions for Porosity Control
Implementing innovative modern technologies and cutting-edge approaches plays a critical duty in accomplishing remarkable control over porosity in welding processes. In addition, using sophisticated welding strategies such as pulsed MIG welding or changed ambience welding can additionally help reduce porosity issues.
Another innovative service includes using sophisticated welding tools. Utilizing equipment with integrated functions like waveform control and innovative power resources can boost weld quality and decrease porosity threats. Furthermore, the execution of automated welding systems with specific control over specifications can substantially reduce porosity issues.
Moreover, including innovative i thought about this monitoring and assessment technologies such as real-time X-ray imaging or automated ultrasonic screening can help in detecting porosity early in the welding process, enabling instant corrective actions. On the whole, integrating these sophisticated options can greatly improve porosity control and enhance the overall high quality of welded parts.
Conclusion
Finally, understanding the scientific research behind porosity in welding is essential for welders and producers to produce top notch welds. By recognizing the variables affecting porosity development and carrying out techniques to lessen it, welders can improve the overall weld quality. Advanced remedies for porosity control can further enhance the welding procedure and ensure a solid and reputable weld. It is necessary for welders to continually enlighten themselves on porosity and apply finest practices to achieve optimum results.
Comments on “What is Porosity in Welding: Typical Resources and Efficient Solutions”